
EEBUS for E-Mobility – A Story of Success
Sector Coupling – The Biggest Driver
The electrification of the transport and heat sector is rapidly increasing. By 2025 we will have more than 5 million electric cars and an estimated 20 million electronic heat pumps in Europe. The likelihood of both devices drawing electricity in the same building and at the same time, and thus overloading the building’s grid connection point, increases significantly. In return, energy flows inside the building must be managed efficiently. For this, EEBUS is increasingly establishing itself as the standard for interoperability in the energy grid inside the building. As a leading EEBUS integrator, KEO has been involved from the very beginning. Since the first Plugfest of the EEBUS Initiative e.V. in Cologne, our EEBUS software stacks have made a significant contribution to the solutions of the future. Ever since, the automotive industry has been a sector we are involved in particular.
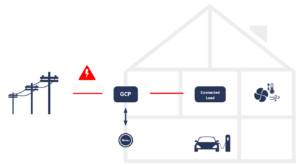
Sector coupling within the building (EEBUS Initiative e.V., 2019)
It All Began in the Name of Research

The EEBUS Initiative has its origin in the first national Smart Grid project in Germany. In the project E-Energy, supported by the BMWi, the first smart grids were tested in six research regions and associated market solutions were developed.
Back then, Spiegel Online described the conversion of the energy system as “probably the largest infrastructure project” of all time.
Within the project, the Smart Watts consortium had the task of achieving end-to-end optimization of the entire energy system – from generation, trade and distribution to the final consumer. Here we developed the first approaches of the connectivity concept EEBUS, which was later adopted by other subprojects (e.g. MOMA). This concept made it possible for the first time to adapt electricity consumption to generation by means of interoperable, technology-independent device control. As an immediate reaction to these successes, the EEBUS initiative was launched shortly afterwards.
Today an Essential Component in the Most Important R&D Projects
However, Smart Watts and E-Energy were just the beginning: In eConnect, a BMWi lighthouse project in the field of ICT and electromobility, we were significantly involved in the first concepts for grid integration of electromobility via the EEBUS communication standard, which has become increasingly well-known in the meantime.
In the subsequent project – called 3Connect – a holistically approach was chosen: An intelligent local load management of a commercial customer acts within given load limitations. It thereby enables smart allocation of the maximum available load over a larger number of charging points. Further, the company’s own renewable energy generation and a local storage battery for optimized charge control were taken into account. In addition, the marketing of the company’s own flexibility was tested. This flexibility was created e.g. by automatically postponing charging processes to the night and reacting specifically to favorable variable electricity tariffs.
In the BMWi funding programme SINTEG, transferable concepts and solutions for a safe, economical and environmentally energy supply with at times 100% renewable power generation are developed and demonstrated. Here, we are currently working on raising EEBUS communication from Smart Building to Smart Grid level. The integration of Smart Metering System (iMSys), as an essential part of a sustainable energy landscape, as well as the development of further use cases, especially those related to e-mobility, play a central role here. In this context, the first Smart Grid Use Cases, such as dynamic power limitations at the grid connection point, will be tested. With our EEBUS integration, we do significantly contribute to the development of an overall architecture from grid to the home and suited for rollout.
From Theory to Practise

Plugfest in Dresden – SMA, EEBUS e.V. and VW test EEBUS communication (SMA, 2017)
‘PV Self-Consumption Optimization’ was one of the first EEBUS Use Cases: It enables the charging station to adapt its consumption to the PV generated in the building in order to realize cost-effective and emission-free charging. The Use Case was presented to the public for the first time at the E-Mobility Plugfest at the VW plant in Dresden.
Automobile Association Now Relies on EEBUS
The VDA, as the representative of the German automotive industry, shortly afterwards committed to EEBUS for connectivity of the EV and the local energy management system (EMS). The association’s architecture makes clear: In the future, efficient energy management is realized using EEBUS as communication among devices and systems. A great advantage: With a single system, that every device is connected with, the grid is provided with a central contact point for every building.
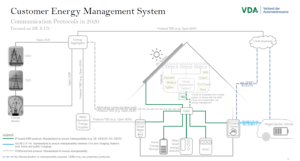
VDA genreral architecture, from grid to device level (VDA, 2018)
The Breakthrough: EEBUS Release for E-mobility

Plugfest in Brussels with renowned participants (Audi, 2019)
After several internal tests and optimizations, the time had come at the beginning of 2019:
At the final “Plugfest E-Mobility”, EEBUS members tested their developments at the Audi plant in Brussels based on the open communication standard. The focus was on testing seamless communication between the PV system, charging infrastructure, electric car and heating. A central EMS connected all energy-relevant devices to allow for an exchange of energy demands and to test new use cases.
Among others, E.ON was testing its Microsoft Azure Sphere based EEBUS energy management system as well as GridX, TQ, Hager and SMA. Further participants were Innogy, Audi, Porsche, Iotecha from New York, the automotive suppliers IAV and Kostal, as well as the heating companies Vaillant and Viessmann. Of course, the two EEBUS stack integrators Bosch SI and KEO were also present, which not only demonstrated that their competitive solutions are technically mature but are also compatible with each other.
EEBUS Has Arrived in The Automotive Market

Audi e-Tron speaks EEBUS (Audi, 2019)
Audi’s announcement of an EEBUS electric car, the open communication standard was lifted to the next level of market maturity, at the beginning of the year. The Audi e-tron is officially the first electric car on the market to support connected and secure charging in compliance with local energy management according to the EEBUS standard.
However, an EEBUS interface will not only be implemented in charging cables, such as those of the Audi e-tron, but also in other components of the EV charging infrastructure, such as wall boxes and charging stations. For example, charging equipment from manufacturers such as Mennekes, Wirelane, eSystems MTG GmbH and Innogy uses EEBUS to communicate with local EMS. Recently one of the leading players in the world of e-mobility has joined: The Dutch manufacturer of charging infrastructure, EV Box, now also uses EEBUS.
EEBUS for a Smart Future in E-mobility
The EEBUS specifications for charging of EVs primarily serves three purposes: overload protection, grid stabilization and low-cost charging with PV electricity.
The EEBUS communication standard defines all these application scenarios and also provides interfaces to other EEBUS applications, for example for the flexible use of heat pumps or household appliances. The recently published White Paper E-Mobility lists all EEBUS E-Mobility Use Cases published up to now and describes them in more detail. The position paper on Smart Home Solutions und digitaler Heizung of the BDH describes the role of EEBUS particularly in Smart Heating. All new E-Mobility Use Cases – tested at this year’s Plugfest – are now available online. Please find the detailed specifications on the website of the EEBus Initiative e.V for free download!
Meanwhile, the EEBUS Initiative is constantly working on new use cases. Here, the focus lies on applications scenarios in the area of bidirectional loading (vehicle-to-grid) and dynamic load limits at the grid connection point. For the latter, the respective EEBUS ‘Working Group’ is in close exchange with the Network Technology/Network Operation Forum at VDE (VDE|FNN) and with numerous distribution grid operators.
-> Want to become part of the global cross-industry network of the EEBUS Initiative? Learn more about EEBUS!
-> Are you interested in an EEBUS implementation? Have a look at our SW solutions!
Author:
